- What is core router and Edge router
?
OSI Layers
- Physical
- Data
- Network
- Transport
- Sesssion
- Presentation
- Application
What happens when you type an url?
This pretty much covers the basics of all major networking concepts. Will go through layer by layer and get some insight
- DNS: get the server address resolved from the website address (This can be taken from browser cache, if not present, make a system call to the OS to get from OS cache, then to router and then to the ISP)
Application layer
Layer where the end user actually interacts with the software
Protocols: HTTP , FTP
Quick things to know about HTTP :
- Works on request reply model
- GET POST are the commonly used http requests
- HTTP cookies are used
- Uses TCP protocol
Presentation Layer
Also called as syntax layer
- Translation: Representation of data might be different in end user system. One end it might be mac, other end linux
- Compression: To increase throughput
- Encryption: Security reasons. Protocol used SSL . Encryption done in lower levels of protocol stack as well called IPSec
Session Layer
The name of this layer tells you much about what it is designed to do: to allow devices to establish and manage sessions. In general terms, a session is a persistent logical linking of two software application processes, to allow them to exchange data over a prolonged period of time. In some discussions, these sessions are called dialogs; they are roughly analogous to a telephone call made between two people.
eg: Socket interface APIs used by transport layer
Transport Layer
Transmission Control Protocol
- Connection oriented - 3 way handshake
- Reliable transmission - order transmission using the sequence number field.
- Flow control - sliding window protocol
- Congestion control - ack, timers
- MSS - set according to MTU so that fragmentation is avoided, path MTU discovery is used to set the MSS accordingly.
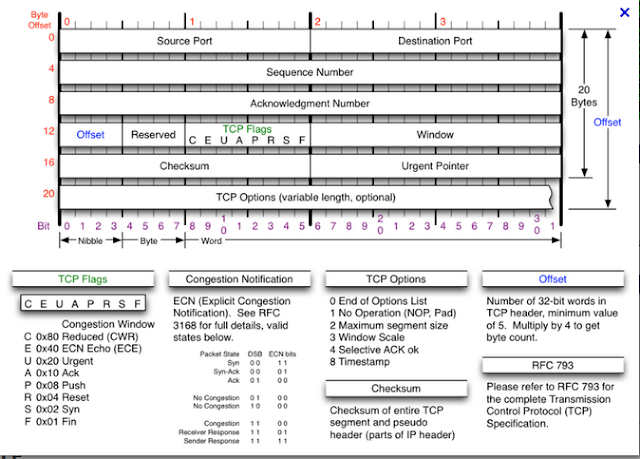
TCP Header
TCP Connection - 3 way handshake

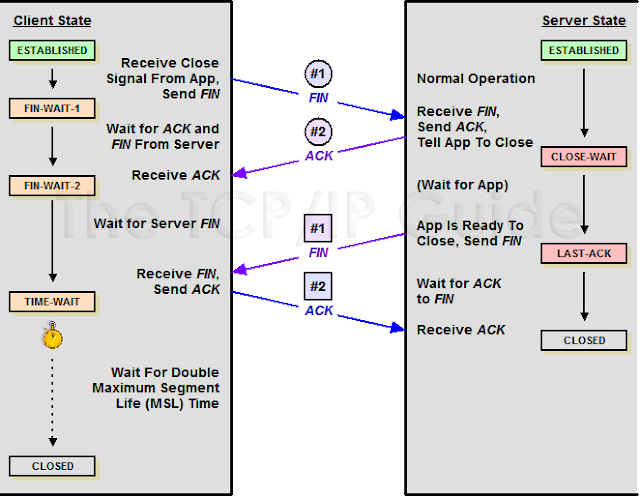
TCP Connection close
 Sliding Window Protocol
Sliding Window Protocol
The TCP urgent pointer is used to push data out of band ahead of already sent data.
Textbook example for that would be a slow telnet session in which after
sending many commands, you decide to abort the session or the command
using a control character such as control-C.
If you do not use an urgent pointer, the control-C will have no effect
since it will have to pend the processing of all of the previous
commands.
Using urgent pointer, the control-C processing is done out of band
BEFORE the other commands, and thus it can cancel them or the entire
session.
UDP header
ICMP header
Network Layer
IPV4 header
IPV6 header
IPV4 and IPV6 header comparison
IPV4
|
IPV6
|
Header size – 20 bytes
|
Header size 40 bytes
|
Addresses 2^32
|
2^128
|
IP checksum
|
No IP checksum
|
32 bits aligned
|
64 bits aligned
|
Broadcast address
|
No broadcast (Use multicast)
|
NAT
|
No NAT
|
Network id/host id
|
Global routing prefix/subnet id/interface id
|
|
|
TCP Socket
UDP Socket
Endian Transformation
- Big Endian - First Byte is MSB, Last byte, LSB Network byte order -ppc
- Little endian - First Byte is LSB, Last byte is MSB - Intel processors
- Convert a given ipv4 address from one endian form to another
Server
|
Desktop
|
No
|
Graphic intensive applications
|
Higher Cache size
|
|
More varied cache
|
|
Multiple cores
|
|
Serveral hard drives configured to appear as a single
disk- RAID (Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks)
|
Single hard drive
|
RPM of disk is more – faster
|
|
Hot Swappable drives
|
|
Faster RAM
|
|
ECC RAM
|
|
Redundant power supplies
|
|
No monitor, keyboard, mouse. Managed via network
|
Managed via monitor, keyboard, mouse
|
1GB n/w interface, multiple n/w interface
|
|
Trunk Port - Carries multiple VLAN frames
References
www.tcpipguide.com
http://beej.us/guide/
http://i.dell.com/sites/content/business/smb/sb360/en/Documents/What-Is-a-Server.pdf